Wool Fibre | Identification & Application of Wool fibre | Part 01
Wool Fibre | Wool Fibre Identification | Uses & Application of Wool fibre
Wool Fibre
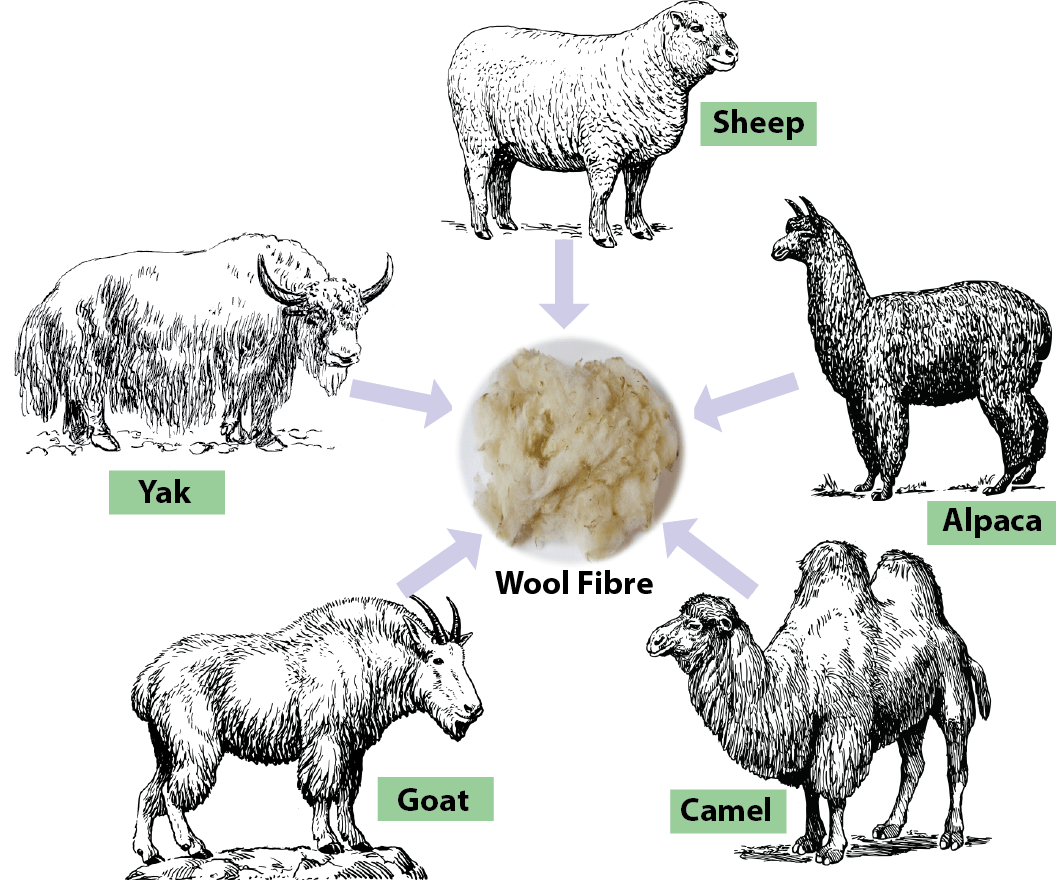
Wool is the natural protein fibre obtained from sheep and certain other animals, including cashmere from goats, mohair from goats, angora from rabbits, and other types of wool from camel. It is a multi-cellular, staple fibre. The density of fibre is 1.31g/cc, which is tends to make wool a medium weight fibre.
Fig: Source of Wool Fibre
Main Wool Producing Countries
The world’s leading animal fibre, wool is produced in about 100 countries on half a million farms. Major wool producers are Australia, Argentina, Canada, China, Chile, France, the Islamic Republic of Iran, New Zealand, Russia, South Africa, Turkey, the United Kingdom, and Uruguay etc.
Here is the list of top 10 wool producing countries in the world 2015.
| RANK | COUNTRY NAME | PRODUCTION (TONNES) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Australia | 478,492 |
| 2 | China | 235,927 |
| 3 | USA | 150,875 |
| 4 | New Zealand | 102,457 |
| 5 | Argentina | 88,897 |
| 6 | Turkey | 74,394 |
| 7 | Iran | 56,990 |
| 8 | UK | 49,623 |
| 9 | India | 31,783 |
| 10 | Sudan | 20,739 |
Wool Fibre Identification
Physical test
The flame is steady but more difficult to keep burning. The smell of burning wool is like burning of hair.
Chemical test
Wool fibre dissolves in concentrated
- Sodium hydro – oxide
- Sodium hypo – chloride
- Slowly dissiolves in Nitric acid 70%.
Uses & Application of Wool Fibre
Wool is extensively used in textile applications where comfort and aesthetics are important. Some uses and application of wool fibre are given below –
Wool fibre used for clothing, blankets, insulation and upholstery.
It is used in men’s and women’s apparel, outer wear and cold weather clothing, suits, blankets, felts and carpeting.
It is often used in blends with cellulosic and man-made fibres.
It is also used for absorb noise of heavy machinery and stereo speakers.
As an animal protein wool, can be used as a soil fertilizers, being a slow release source of nitrogen.
End uses of wool fibre
Alpaca fibres are used for many purposes, including making clothing such as hats, mitts, scarves, gloves. And jumpers. Rugs and toys can also be made from alpaca fibres. Alpaca fleeces is generally used only in the expensive luxury items of textile and apparel
Lama fibres are used in expensive knitted fabrics, jackets, over – coats, and blankets.
Camel hair is used for outer wear and used for under linings
Cashmere is used in luxury applications where a soft, warm, fine fibre with beautiful drape is desired.
Mohair is used for outer – wear.
Difference Between Silk & Wool Fibre
SUBJECT
|
SILK
|
WOOL
|
Composition
|
It has carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen. It is attacked by carpet beetles.
|
It has hydrogen, carbon, Sulphur and nitrogen. It is harmed by moths and beetles
|
Elasticity
|
It has extended poly peptide chains and is less elastic and resilient.
|
It has folded poly – peptide chains and more elastic and resilient.
|
Strength
|
It is very crystalline and is less absorbent.
|
It has more amorphous areas and more absorbent.
|
Dimensional Stability
|
It is a solid fibre.
|
It has four parts in its fibre structure and therefore shrinks and felts.
|
Texture
|
It is smooth. White silk is smoother and more lustrous.
|
White wool fibre has crimp which is molecular. Therefore, wool is warmer and more resilient.
|
Length
|
It is usually a filament and is smooth.
|
It is staple fibre and is fuzzy.
|
Hydroscopic nature
|
Since it has a very crystalline polymer system, it is less absorbent than wool.
|
It is more absorbent.
|
Thermal properties
|
It is more sensitive to heat.
|
It is less sensitive to heat.
|
Effect of acids
|
It is degraded more than wool because of absence of disulphide bonds, perspiration which is acidic will cause breakdown of silk polymer.
|
It is degraded less than silk.
|