Basic Concept of Combing Process | Types of Comber Machine
Basic Concept of Combing Process | Types of Comber Machine
What is Combing?Combing is the process that removes the final proportion of short fibers, neps and others impurities such as vegetable matter and seed coat fragments in cotton that has already been carded. Combed yarns are superior in quality when compared to carded yarn as they are generally finer, stronger, smoother and more uniform due to the removal of short fibers and the alignment of fibers.
Task of the Combing Process :
To remove pre-determined length of short fiber (noil%)
To remove neps
To remove remaining impurities
To straightening hook fiber
To remove neps
To remove remaining impurities
To straightening hook fiber
Why Combing is Essential to Produce Fine Yarn
1. For finer count, high draft is required but short fiber create draft irregularity. After combing short fiber is removed for higher draft for the next step.
2. Longer fibers are finer than short fibers. After combing higher count is possible to keep minimum no. of fiber in yarn dia.
3. Long fiber yarn has less hairiness but more luster.
4. Combing is necessary for better yarn appearance and regularity.
Effect of combing on yarn and fabric quality
Improve the spinning value of fiber
Better twist distribution improve the strength of yarn
Improve uniformity, smooth and luster of yarn
Reduce yarn hairiness and imperfection
Produce short trash free clear yarn
Improve efficiency in the next process
Improve yarn regularity & strength
Better twist distribution improve the strength of yarn
Improve uniformity, smooth and luster of yarn
Reduce yarn hairiness and imperfection
Produce short trash free clear yarn
Improve efficiency in the next process
Improve yarn regularity & strength
Importance of fiber arrangement in card sliver
To reduce the strain to delicate comber reduce
To reduce fiber damage
To reduce chance of good fiber waste
To reduce short fibers- To reduce thick and thin paces in the sliver
To control wastage
To parallel and straight of fiber in carded sliver by changing pushing of fibers
Not freely opening of fiber from sliver
To reduce fiber damage
To reduce chance of good fiber waste
To reduce short fibers- To reduce thick and thin paces in the sliver
To control wastage
To parallel and straight of fiber in carded sliver by changing pushing of fibers
Not freely opening of fiber from sliver
Conditions of stock preparation before combing:
- Fiber parallelization
- Even no. of passage between card and comb
Types of Comber Machine
Many different types of combers are used for different fibre materials, combers can be classified into following types:
- Rectilinear Combers (used for cotton)
- Circular Combers (used for worsted)
- Rotary Combers (used for spun silk)
- Hackling Machines (used for bast fibers)
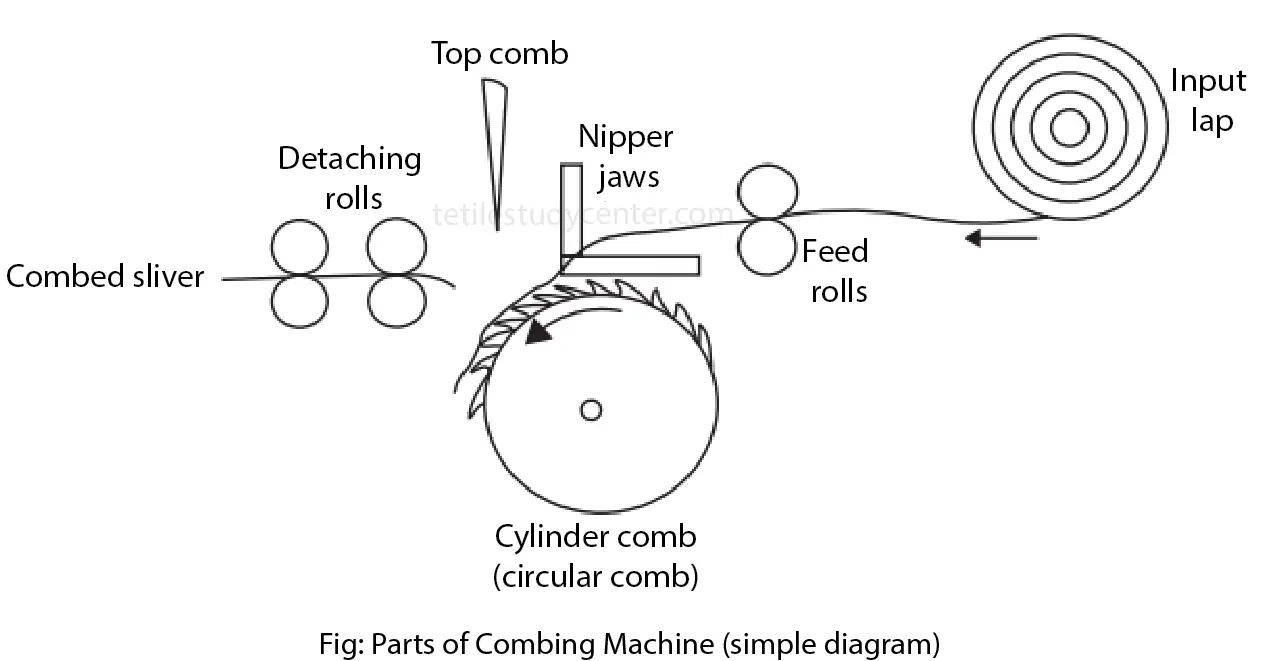
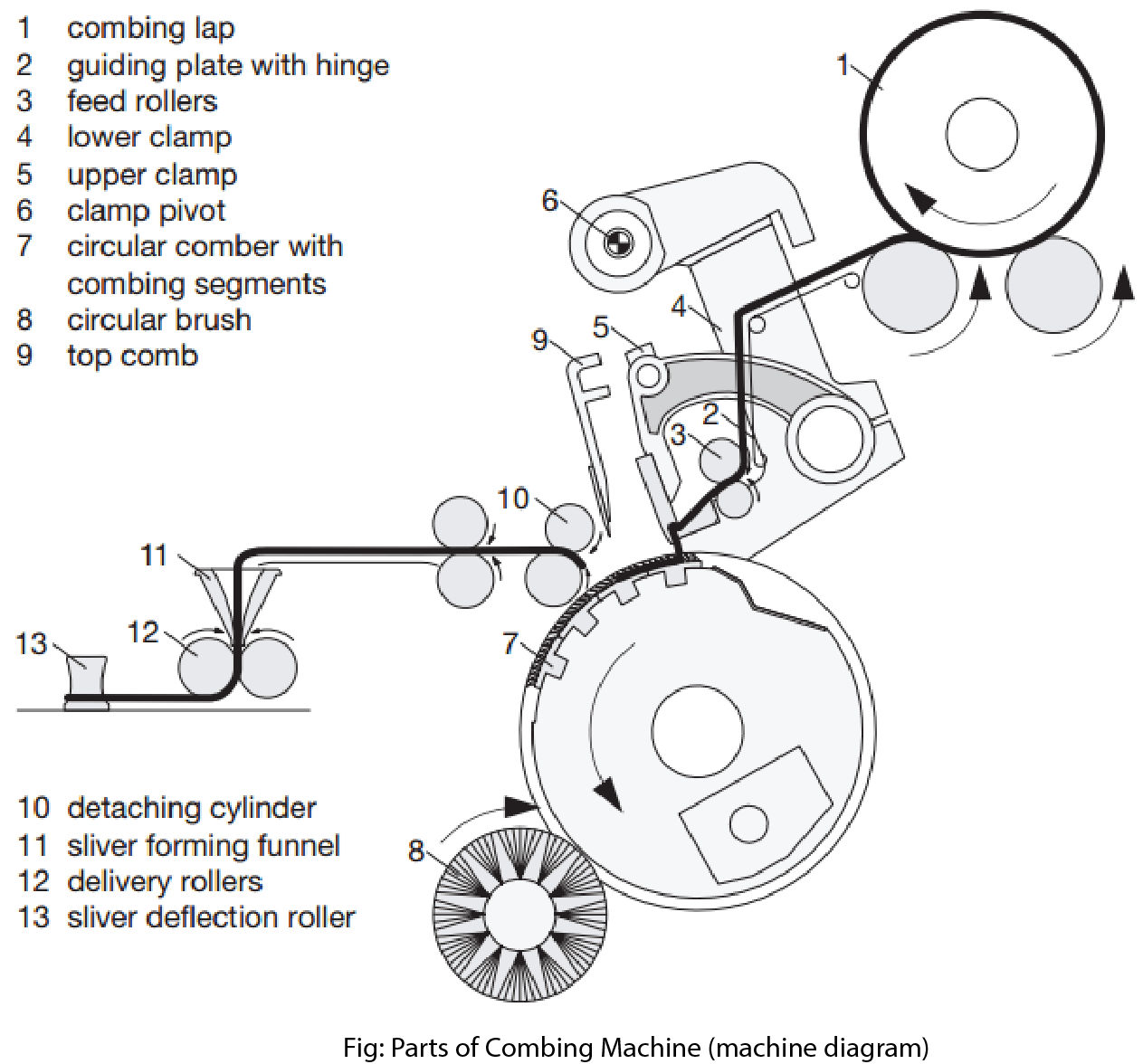
Basic Working Elements of a Combing Machine
The web rolled off from the lap (1) is pinched between the lower (4) and the upper clamp (5).
The circular comber covered with combing segments (7) combs out the fiber beard that is protruding from the clamps. The short fbers that are now sticking in the circular comber are removed from the combing segments with a brush (8).
Afer the combing action, the upper clamp rotates upwards. The clamps are now open. Upper and lower clamps swing around the pivotal point of the clamps (6) toward the detaching rollers (10). The detaching rollers grab the fiber beard and attach it to the previously combed fibers as a continuous fiber web. This action is called soldering.
After soldering, the top comb (9) moves down into the fiber beard so that the detaching rollers do not pull out the web from the clamps during the detachment. With the transporting movement of the detaching rollers, the web is separated; this is called detachment. The detachment is supported by the clamps swinging backwards.
Prior to the next combing sequence, the delivery rollers (12) transport the web forward through the open clamps at an adjustable feed rate. On closing of the clamps, the next combing sequence starts.