Terry towels – fabrics that can absorb large amounts of water
Design, manufacturing, and technological features of terry towels
A terry towel is a textile product which is made with pile loops on one or both sides covering the entire ground surface or forming pile strips, pile checks, or other pile patterns (with hemming end or with firm selvedges).

A terry towel is a textile product which is made with pile loops on one or both sides covering the entire ground surface or forming pile strips, pile checks, or other pile patterns (with hemming end or with firm selvedges). Turkish Toweling fabrics structures form a class of warp pile termed terry pile in which certain warp threads form loops or curls on the face of the cloth. We may use one weft and two series of warp threads placed on two warp beams are necessary for the production of this cloth.
Cashmere Towels are made of Superior Ring Spun Quality Yarn. They are soft and luxurious and will provide a sense of comfort to your valued guests. Cashmere Towels are the best choice you will make by balancing luxury and cost.
History of Terry Weaving
The invention of the towel is commonly associated with the city of Basra, Turkey in the 17th century. These Turkish towels began as a flat, woven piece of cotton or linen called a pestamel, often hand-embroidered. The name word terry came from French word tire which referred to pile loops which were initially pulled by hand Long enough to make it absorbent cloth and wrap around the body. These pestamel manufactured were originally fairly narrow, but now are wider and commonly measure 90 by 170 centimetres (35 in × 67 in). Pestamel were used in Turkish baths as they stayed light when wet and were very absorbent.
Fibre Raw materials used for terry towels
- Cotton
- Bamboo
- Model
- Lyocell
- Flax
- Synthetics microfibers (polyester, nylon)
- Cashmere
Yarns used for towels
 Both open end and ring spun yarns can be used depending on designing parameters of terry towels. Normally three yarn components are used in manufacturing terry towels. Normal twisted yarn with normal twist factor for ground yarn, low twisted yarn with lower twist factor for pile yarn and low twist or normal twisted yarn for weft yarns.
Both open end and ring spun yarns can be used depending on designing parameters of terry towels. Normally three yarn components are used in manufacturing terry towels. Normal twisted yarn with normal twist factor for ground yarn, low twisted yarn with lower twist factor for pile yarn and low twist or normal twisted yarn for weft yarns.
Single or double yarns are used for all or few yarn components again depending on how the product has been designed. To make towels more absorbent and soft, twist less cotton ring spun yarns are also used.
For producing twistless yarn, cotton ring spun yarn with very low twist factor is covered with a water-soluble PVA filament yarn on yarn covering machine or is twisted on TFO machine the direction of double yarn twist is opposite to that of the single spun yarn twist, and the amount of twist factor is adjusted to normal twist required in the spun yarn. By this process, the PVA filament wrapped around the cotton yarn and the yarn was sufficiently strong due to the cohesion has given by the filament which makes it weave able and during finishing operations, the PVA yarn is dissolved in water.
Types of bath towels
| Towel type | Size | Best Uses |
| Bath Towel | From 27″ x 52″ to 30″ x 58″ |
|
| Bath Sheet | From 35″ x 60″ to 40″ x 70″ |
|
| Hand Towel | From 16″ x 28″ to 18″ x 30″ |
|
| Finger Towel | 11″ x 18″ |
|
| Washcloth | About 13″ x 13″ |
|
Classification of Terry Towels
The classification of towels can be made according to construction, dimensions, pile presence on fabric front and back surfaces, pile height formation, pile structure, finishing and weight per square meter. These classifications are shown in Table
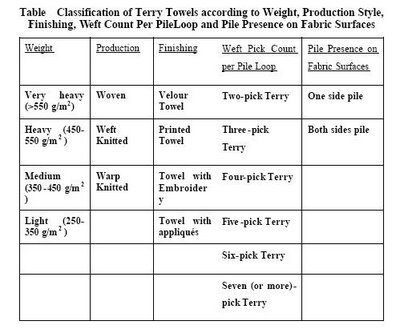
In velour towels, pile loops on one side of the fabric are sheared in order to give a smooth velvet appearance, good drape and improve upon absorbency. A towel with appliqués is embellished with additional pieces of decorative fabric in a motif which is stitched onto the towel. Two-pick terry towels which were woven for bathrobe end-use have lost their importance today due to the instability of the loops.
Five or more pick terry towels are rarely produced because they need to be beaten for each pile twice. The most common towels woven are three pick terry towels and are universally accepted. As one-sided pile towelling has low water absorbing and visibility of more defects like bareness, irregularity etc. Towels are classified according to end use and dimensions as bath towels, hand towels, face towels, fingertip towels, kitchen towels and washcloths.
Construction
Terry towels are woven as 2, 3, 4, 5 or more pick terry weaves. The most common type is 3-pick terry towelling. The cross-section of a towelling through the Warps are divided into two systems as shown in Figure 3, pile warps and ground warps, whereas wefts consist of only one system. In basic Turkish Toweling, front side and back side pile warps and 1st and 2nd ground warp end form a 2/1 rib weave with each other.
The rib weaves which is formed by the pile warps is one pick ahead of the rib weave which is formed by ground warp ends. Warps are drafted throughout the fabric width 1:1 or 2:2 piles and ground warps. In 1:1 warp drafting order each ground warp end is followed by a pile warp end while in 2:2 warp drafting order each two ground warp ends are followed by two pile warp ends. In Figures 3a and 3b, the weave notation of 3 weft pile basic Turkish towelling is given in 1:1 and 2:2 warp orders.
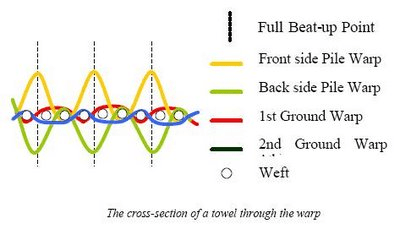
As is seen from the weave diagrams in Figures a and b, the shedding of the ground warps is not synchronized with that of the pile warps. By this, the number of interlacing throughout the warp increases, and this strengthens the fabric. As it has been mentioned before terry towels can have pile loops on one or both faces. Different types of terry weave which have piled on one face and both faces.


G: Ground Warp
FP: Front Face Pile Warp
BP: Back Face Pile Warp
Little block: Ground warp is over the weft
Shaded: Front Face Pile Warp is raised over the weft
X: Back Face Pile Warp is raised over the weft
Empty space: Warp is lowered behind the weft
FP: Front Face Pile Warp
BP: Back Face Pile Warp
Little block: Ground warp is over the weft
Shaded: Front Face Pile Warp is raised over the weft
X: Back Face Pile Warp is raised over the weft
Empty space: Warp is lowered behind the weft
The picks used for towelling is between 15 and 25 picks/cm. And ends used are between 20 and 30 ends/cm. During the weaving of borders, the picks are increased 3 to 6 times the density in the pile areas Pile/ground ratio is described as the length of pile warp per unit length of fabric in the warp direction.
A practical way to find out this ratio is done by measuring a 10 cm length of towelling in the warp direction, then cut the pile warp from either end of the measured length and measure the total length of the removed pile end per 10 cm length of fabric. Pile warp length per 10 cm fabric is usually between 20-100 cm. This ratio has a direct effect on the fabric weight and thickness. As the ratio increases, the weight and the thickness of the terry fabric increases.
Manufacturing process
Spinning
This is the process where selected fibres are converted to yarns of desired counts needed for towels. Some integrated textile towelling mills produce their own yarns for towels. They purchase bales of cotton of a specific grade as per their working plan.
- Mixing of fibres are formulated as per the required plan and are subjected to required atmospheric conditions before they are passed through blow room line. Here strictly mill mixing plan is being followed. According to the mix plan selection of machines to process and their machine settings are made before mixing is allowed to pass through blow room line.
- Once planned results in the blow room process are accomplished then these fibres are passed directly through chute feeding to well-set carding machines and fibres are converted into slivers.
- These carding slivers are tested for various technological parameters before they are passed to next process Drawing frames. These draw frames are set as per working plan and slivers are passed through for effective blending and parallelization of fibres. Draw frame slivers are tested for parameters and if passed they are further processed. Draw frame slivers may be semi-combed then again passed through draw frames before they are fed to roving frames (Speed frame).
- Slivers are converted to rovings of specified hank as per spinning plan. Thereafter these roving bobbins are fed to ring frames well set with technological parameters as per spinning plan where they are converted to particular yarn counts to be used for terry towels.
- These ring bobbins are fed to automatic winding machines where the yarn is converted to packages. These winding machines are also ser for different setting required as per spinning plan.
- Whenever double yarns are needed for weaving terry towels the single yarns are processed on TFO machines to convert them to double yarns with defined twist factor and direction of the twist as required for towels.
Preparation of spinning plan is very critical and needs a lot of knowledge and understanding of spinning technology. Application of this spinning plan determines yarn parameters and yarn quality and hence needs a close supervision from process control and quality control laboratory.
Weaving
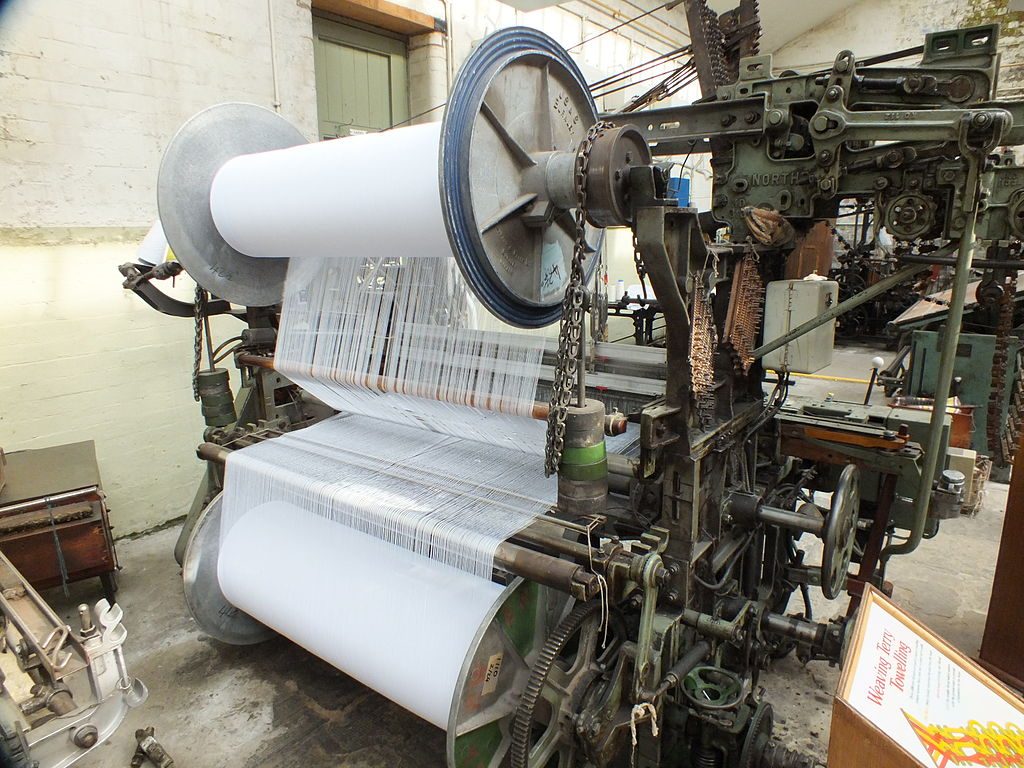

Comprehensive Weaving manufacturing plan is prepared as per terry towel set and construction.
Warping/Sizing/Drawing-in
Yarn packages are assembled on warping creel as per construction plan, required tensions are set on each yarn package and are processed on sectional or direct warping machines depending on single/double yarns are used.
All machine settings, machine speed is set as per instruction sheets of weaving plan. All warping sets made from single yarns are processed on sizing machines where a starch coating is applied on individual threads to make it weave able on weaving machines. Double yarns sets may or may not be passed through sizing machines. Single sized beams and double sized or unsized beams are taken to drawing in department and beams are drawn as per drawing in weaving plan to make them ready to load on weaving machines.
Loading of beams is high skill jobs which are to be carried out under the close supervision of weaving staff. Before machines are loaded on weaving machines, machines are to be well set, speeds adjusted as per article by experienced, skilled and qualified weaving staff. Use of machine setting sheets as per weaving set plan is essential and important before the machine is set for production. Process control staff and weaving senior staff has to monitor the initial production of few towels and inspect on the machine and off the machine the various parameters of the towel and should exactly match as per weaving plan. Once passed the machine is allowed to go into production.
Mechanism of terry weave in terry fabric manufacturing, two sheets of warp threads run simultaneously, of which, one is kept under normal tension and other is kept under loose tension. The threads of normal tension warp sheet are for ground and threads of loose tension warp sheet are for the pile.
The sequence of operations during weaving for pile formation in 3-pick terry is given below:
- Insertion of the first pick as per the design with loose beating
- Allow a predetermined gap near the feel of cloth
- Insertion of the second pick following the first pick with loose beating
- Insertion of the third pick with heavy beating and bring all the three picks to the fell of cloth.
Pile formation
Pile of the towel plays major role for a towel for its water absorbency and other properties. Loop length is decided by the quality, weight etc. as per requirements. Pile manufacturers use better quality yarn like combed, compact, hydro, zero twisted yarns.
RELATED POSTS
Piles are made by different high-value fibres like superior qualities of cotton suvin, giza, pima, bamboo, modal etc. to get better absorbency and lint properties.
For ground yarn, comparatively coarser counts are used in OE and 2-ply option to give better strength and compactness in ground fabric.
Both piles and ground yarns are prepared in the same manner of warping, sizing, and drawing-in. Like other textile products shirting, suiting, sheeting fabrics, towel making has the same process sequences – desizing, bleaching, dyeing and finishing.
Grey inspection
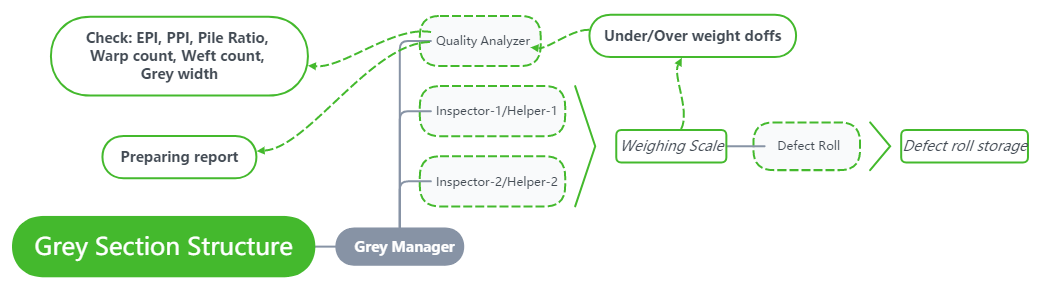
Once towels are manufactured on the looms and their production is monitored through process control the towel roles are cut as per specification sheet and brought to inspection room.
From inspection room storage selected quality rolls passed for quality as per processing plan are dispatched to process house for bleaching and dying operations.
Bleaching
These selected rolls are transported by using recommended trolleys to bleaching section and are bleached in J-Box machine which is a continuous bleaching machine. The fabric is treated with bleaching recipes such as hydrogen peroxide, caustic defoamers and other ingredients.
Reaction time and machine speed have to be set as per process plan prepared after considering all activity factors. After the roll is bleached it is sent to washing machines and washed thoroughly so that no trace of chemicals remains on the fabric. Then these rolls are dried and sent to Dyehouse. All procedural requirements are followed so that the rolls can be identified at any stage during processing and in storage.
Dyeing
As per requirement order from dye house, bleached rolls are transported to dye house for dying operations for various colours as per dye house planning sheets. Dried uncut rolls are taken to Dying machines for dying with vat colour using vat dye receipt. This has proven over time to provide colourfast towelling after extensive residential laundering.
It is sent to washing machines and washed thoroughly so that no trace of chemicals and lose dye particles remain on the fabric. Then these rolls are dried on an air-drying machine and sent to folding cutting/folding and packaging department. All procedural requirements are followed so that the rolls can be identified at any stage to avoid mix-ups during processing and in final storage.
Cutting, folding, and packaging
As per final inspection plan, rolls are transported with special care to finish folding department.
Instruction techniques to follow are for visual inspection
- Step 1: is to open these rolls and are cut as per instruction sheets
- Step 2: is to stitch / ham towels
- Step3: Each towel stitched is inspected by quality inspector attached to a respective table. He has to ensure defect free towel on both sides, the label for passing and sent to final inspection table. The rejected towels are to be kept separately for operational departmental inspection
- Step 4: Final inspection by a senior inspector passed, labelled and sent for final packaging and dispatching. Rejected towels are kept separately.
Quality Control
Quality assurance department plays an important role to monitor, check, and control each manufacturing activities and operations from receiving all raw material to the final dispatch of products. This is controlled through close supervision and active participation of on-line process control and off-line quality control laboratory. Most common defects found in terry towels are…
Objectional odours, Holes (two or more broken ends), abrasion mark, Bow, Skew, crease, oil stains, dye stains, miss pick, double picks, sharp press mark, fibre contamination, dye/bleach shade variations.
All Towels manufacturing mills need to have a strong quality assurance department which is capable to coordinate with production line and assist them to provide vital quality productivity information continuously.
All incoming inputs bought for manufacturing process are thoroughly examined for their quality parameters as laid down by production plan before they are used during manufacturing operations.
Caring for your Towels
- Wash towels at between 40-60°C
- Wash with similar colours or use a colour catcher
- Tumble dry towels to keep them soft and fluffy
- Use fabric conditioners sparingly and not in every wash as they decrease absorbency
- Wash separately from garments with zips or trims to avoid snagging
- Shake towels before washing –this opens up the fibres slightly to allow the detergent to sink inside.
Key points to focus during production planning
- Customers support. Fully understanding customers requirements and their expectations.
- Process control providing products utilizing proven designs and manufacturing process.
- Top employees developing a highly trained workforce that is skilled, motivated, understandable, empowered and fully accountable.
- Robust supply chain: establishing strong relationships with world-class suppliers
- continuous improvement: continually improve the efficiency of the business processes and operational activities and operations, quality management systems.
Calculations for terry towels to find the weight of ground warp, pile warp and weft yarn
Assumptions
- Number of Ground Warp Ends = 694
- Ground Warp Count = 25 tex x 2
- Warp Crimp = 8%
- Weft Yarn count = 34 tex
- Number of Pile Warp Ends = 576
- Length of pile part = 102 cm
- Pile Ratio (for pile height)= 52:10 (52 cm of pile warp for 10 cm of cloth)
- Pile Yarn count = 30 tex x 2
- Length of plain part = 4 cm
- Picks per cm = 20
- Reed Width = 58.4 cm
- Grey Length ( Pile and Plain Part) = 106 cm
- Fringe Length = 2 cm
Calculation-1
The weight of Ground Warp = Weight of ground warp in grey cloth + weight of ground warp in the fringe.
Weight of ground warp in grey cloth = (length of grey cloth x warp crimp factor x no of ground warp threads x warp yarn count in tex )/ (100 x 1000)
= (106 x 1.08 x 694 x 25 x 2)/(100 x 1000)
= 397.25 gms
= (106 x 1.08 x 694 x 25 x 2)/(100 x 1000)
= 397.25 gms
Weight of Ground Warp in Fringe (here the warp crimp is not involved) = (Fringe length x no of ground warp x yarn count in tex)/ (100x 1000)
= (2 x 694 x 25 x 2)/ (100 x 1000) = 0.69 gms
= (2 x 694 x 25 x 2)/ (100 x 1000) = 0.69 gms
So Ground Warp Weight = 397.25 +.69 = 397.94 grams.
Calculation-2 (continued from terry towel calculation-1)
The weight of Pile Warp = weight of pile warp in pile part + that in plain part + that infringe
a. Weight of pile warp in pile part ( Pile ratio: 52:10)=( Length of pile part x number of pile threads x pile length x yarn count in tex) / (100 x 1000)
= (102 x 576 x 52 x 30 x 2)/(100 x 1000)
= 183.31 g
a. Weight of pile warp in pile part ( Pile ratio: 52:10)=( Length of pile part x number of pile threads x pile length x yarn count in tex) / (100 x 1000)
= (102 x 576 x 52 x 30 x 2)/(100 x 1000)
= 183.31 g
b. Weight of Pile warp in Plain Part
=( Length of plain fabric x number of pile threads x crimp factor x yarn count)/ (100 x 1000)
= (4 x 576 x 1.08 x 30 x 2)/(100 x 1000)
= 1.49 g
=( Length of plain fabric x number of pile threads x crimp factor x yarn count)/ (100 x 1000)
= (4 x 576 x 1.08 x 30 x 2)/(100 x 1000)
= 1.49 g
c. Weight of Pile warp in fringe ( No crimp , no loop )
= (fringe length x number of pile threads x yarn count)/(100 x 1000)
= (2 x 576 x 30 x 2)/(100 x 1000)
= 0.69 g
Weight of pile warp = 183.31+ 1.49 + 0.69 = 185.49
= (fringe length x number of pile threads x yarn count)/(100 x 1000)
= (2 x 576 x 30 x 2)/(100 x 1000)
= 0.69 g
Weight of pile warp = 183.31+ 1.49 + 0.69 = 185.49
How to Determine the Weight of Weft in Terry Towel
The weight of Weft Yarn
= (Total no of weft threads x reed width x yarn count)/(100 x 1000)
(Reed width is equal to the length of one weft yarn)
= (106 x 20 x 58.4 x 34)/(100 x 1000)
= 42.09 g
= (Total no of weft threads x reed width x yarn count)/(100 x 1000)
(Reed width is equal to the length of one weft yarn)
= (106 x 20 x 58.4 x 34)/(100 x 1000)
= 42.09 g
What is GSM?
GSM is the short form for grams per square meter. All fabrics including towels have a measurement in weight, and the standard measurement is measured in grams per square meters. This number refers to the density of the towel. High-quality Turkish cotton towels are generally heavier and are more absorbent.
Towels can vary anywhere between 300 GSM and 900 GSM. The lower the number, the lighter and thinner the towel. For instance:
300-400 GSM – In this weight category the towels are lighter and thinner. Depending on its use, a lower GSM for the towels are manufactured for gym towel or a kitchen towel. A lightweight, shared beach towel might be around 350 GSM. Medium weight is 400-600 GSM. This weight is great for beach towels, bath towels, guest towels and so forth. Each consecutive gram weight –400, 500, 600– gets a little heavier, and a little more absorbent.
600-900 GSM – This is a premium, luxury weight. The towel will be denser, heavier, more absorbent. It will probably take a little longer to dry.
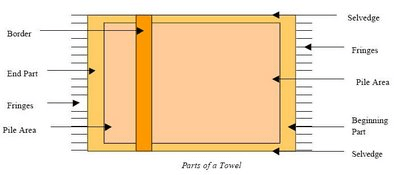
Parts of a Conventional Terry
A woven towel consists of five parts. These are the pile area, fringes, beginning and end part, selvedge, border. Every towel does not have to contain all of these parts. The pile area is considered the towelling part of the towel. Fringes are tied or an untied tasselled part of ground warps and pile warps which are left unwoven at the beginning and the end edges of the towel. The beginning and end sections are the tightly woven areas of a towel which come before or after the pile fabric part and prevent this pile area from unravelling. They are woven without pile loops, in a flat weave construction. The selvedge contains a fewer number of warp ends than the pile area, for example, 90 compared to 4000 total warp ends, woven without pile as a flat weave and has the purpose to reinforce the towel sides








